
Interim Budget 2024
- Posted by admin
- On 02/02/2024
- 0 Comments
KNAV Budget Review
Union Interim Budget 2024-25
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman presented the Interim Budget 2024-25 ahead of the General Elections. The government followed the status quo as it did in 2019 by withholding any major announcements or reforms considering the budget’s status as Interim. “Sabka Saath, Sabka Vikaas and Sabka Vishwas” turned out to be the theme of this year’s budget stressing on the government’s commitment towards inclusive and sustainable growth. The government reinforced its intent towards a “Viksit Bharat” by 2047. This journey of 23 years marked as the “Amrit Kaal” is expected to be driven by green growth for a sustainable future for all. Furthermore, the government strengthened its goal of narrowing the fiscal deficit with an estimated Debt-GDP ratio of 5.1% in FY 2025 as opposed to 5.9% in FY 2024.
1. Agriculture
- Agriculture sector accounts for 15% of the country’s GDP as per estimates. In India, agriculture and allied sectors have recorded a growth rate of 4% YoY in recent years.
Source: Economic Times
- Prominent voices from the AgriTech startup community had expressed expectations on fostering sustainable growth in the agricultural sector. In addition, the founders had expressed desire to incentivize private equity investments in the agricultural sector.
- The sector continues to remain one of the primary points of focus for the Government as evidenced by the announcement of new schemes for the farmers across the country.
- With this, the Interim Budget 2024 and the upcoming Union Budgets shall continue to shape the trajectory of India’s booming AgriTech Industry.
- In line with the government’s vision to make India a “developed country” by 2047, the government has stressed on four communities namely Poor, Women, Youth and Farmers. This emphasis on the farmers indicates the government’s strong commitment in revolutionising the agricultural sector and uplifting the farmers out of traditional practices towards advanced technological practices.
- The government’s allocation for the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmer’s Welfare stands at INR 1.27 Tn. In context with allocations for other ministries, the corpus stands at the bottom of the pyramid, with defence occupying the topmost spot with INR 6.1 Tn.B. Agricultural Sector Outlook
a. Budgetary Allocation Trend1
Note: Data is across ministries. Data is actuals except for 2022-23 (Revised Estimates) and 2023-24 (Budget Estimates).
In FY 2024-25, the budgetary allocation has recorded a dip of INR 0.17 Tn, raising concerns about the adequacy of allocation.
Source: Mint
- Agriculture Terms of Trade
As per a 2023 Niti Aayog Study, the terms of trade which represents the ratio of agricultural prices to non-agricultural prices have moved sharply in favour of agriculture in the last decade. This clearly indicates a rise in the incomes for the average Indian farmer. This fact is further substantiated by the Finance Minister’s announcement of the Government’s commitment to hike MSPs for the farmers.
Source: Mint
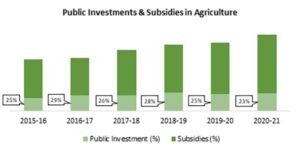
- Investment & Subsidies
The study also delves into the necessity for further development of agricultural markets, warehouses, preprocessing facilities, ripening units and cold storage. This is extremely crucial for the growth of the AgriTech industry at large as it would enhance supply chain management and reduce supply chain wastages. The infusion to meet these requirements is dominated by subsidies at present. There exists a pressing need to induce public investment to facilitate this growth.
C. Existing Measures
- PM-KISAN SAMMAN Yojana provides direct financial assistance to 8 Cr farmers, including small and marginal farmers. In addition, approximately 4 Cr farmers benefit from the Crop Insurance under PM Fasal Bima Yojana.
- In addition, Electronic National Agriculture Market has integrated 1361 mandis, and is providing services to 8 Cr farmers with trading volume of INR 3 Lakh Cr.
- Through these schemes, the government aims to boost agricultural productivity and farmers’ incomes by promoting digitization and automation and mitigating risks.
D. Proposed Reforms & Schemes
- To herald Amrit Kaal, the Government will promote private and public investment in post-harvest activities including aggregation, modern storage, efficient supply chains, primary and secondary processing. This move shall ignite positive reaction in the startup and investor community alike, thereby rallying the two important stakeholders in the AgriTech industry.
- The government announced the application of Nano DAP in all agro-climatic zones. Nano DAP is a nanotechnology based agricultural input providing nitrogen and phosphorous to plants. This move is expected to further the penetration of smart farming in India, while simultaneously furthering government’s goal for sustainable practices in agriculture.
- To capitalize on India’s strength as the world’s largest milk producer, the government will deepen its efforts to increase low productivity of milch-animals and control foot-mouth diseases. Together, these steps are meant to accelerate the pace of growth for DairyTech startups.
- The government has touched all subsectors under the AgriTech fold including aquaculture. Post the particular focus towards the Fisheries segment, India has doubled its seafood production. To continue the momentum achieved in the aquaculture industry, the government has announced establishment of 5 aquaculture parks and set targets for production and exports.
- Together these measures act as a status quo to the government’s longstanding commitment with respect to boosting productivity by enabling infrastructure and incorporating technology.
- In addition, the government’s steps act as answers to the expectations of the investor community with respect to accelerating investment in the AgriTech industry.
2. Infrastructure
Over the past four years, a substantial tripling of the capital expenditure outlay has occurred, resulting in a significant multiplier impact on economic growth and employment creation.
The outlay for the upcoming year is set to increase by 11.1%, amounting to INR 11.1 Lakh Cr, constituting 3.4% of the GDP.
A. Impact on Individual Sectors
a. Railways Sector
- Three major economic railway corridor programmes will be implemented. These are:
- Energy, Mineral and Cement Corridors,
- Port Connectivity Corridors, and
- High Traffic Density Corridors.
- The projects aim to enable multi-modal connectivity, enhance logistics efficiency, reduce costs, and alleviate congestion in high-traffic corridors.
- Additionally, the conversion of 40,000 rail bogies to Vande Bharat standards is planned to enhance safety, convenience, and passenger comfort.
- Railway sector growth drives demand for materials like steel, cement, and machinery, benefiting manufacturing. Improved rail connectivity boosts efficiency in transporting goods, aiding logistics and transportation companies.
- Higher energy demand supports the energy sector, encompassing electricity and transportation fuel. Enhanced rail networks positively impact the agriculture sector by streamlining the movement of products to markets.b. Aviation Sector
- The aviation sector has experienced significant growth in the past decade, with the number of airports doubling to 149.
- Air connectivity to tier-two and tier-three cities has expanded under the UDAN scheme, with 517 new routes serving 1.3 Cr passengers.
- Indian carriers have proactively ordered over 1000 new aircrafts to meet growing demand.
- Expansion of existing airports and the development of new ones will continue at an expedited pace to accommodate the increasing demand for air travel.c. Housing Sector
- The allocation for PMAY (Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana, Grameen) increased from INR 79,590 Cr in 2023-24 to INR 80,671 Cr in 2024-25.
- The Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (Grameen) is nearing the achievement of its target to provide 3 Cr houses, with an additional goal of 2 Cr houses set for the next five years. This progress highlights substantial strides in addressing rural housing needs.
- In a prospective move, the government plans to introduce the Housing for Middle-Class scheme. The scheme is to help deserving sections of the middle class “living in rented houses, or slums, or chawls and unauthorized colonies” to buy or build their own houses.
- The commitment to housing growth will also will concurrently impact the industrial and construction sectors in the following ways:B. Overall Trends Spotted
-
- a. Robust Order Books:
Increased housing initiatives result in heightened demand for construction projects, ensuring a robust order book for construction, infrastructure and realty companies. - b .Lower Gestation Periods:
Achieving housing targets may reduce project gestation periods, positively impacting labour availability and efficiency. - c. Consumer Durable Boost:
Targeting the middle class in housing schemes stimulates consumer confidence, leading to increased sales of white goods and consumer durables. - d. Growth in Industrials:
The emphasis on housing drives demand for construction materials. This will result in pre-emptive capacity expansion and may lead to a trend of increased consolidation among companies involved in the sector.
- a. Robust Order Books:
-
c. Strengthening the Defence
To fortify the defence sector, the incorporation of technology for diverse purposes is crucial. The government shall be introducing a program aimed at integrating the application of advanced technologies in defence. It shall prove to be a crucial step reinforcing “Atmanirbharta”.
The sector has been allocated the highest amount, totalling INR 6.2 Lakh Cr, in contrast to the previous year’s budget of INR 5.94 Lakh Cr.
3. Green Energy & Sustainable Development Initiatives
A. Boosting Wind Energy
To encourage the growth of renewable energy sources, the government is providing viability gap funding for wind energy projects. This initiative aims to make wind energy more financially viable, fostering its development and contribution to the energy mix.
b. Diversifying Energy Sources & Blending Gases for a Greener Mix
- In a bid to diversify the energy landscape, the government is taking steps to set up coal gasification and liquefaction capacity. Coal gasification and liquefaction capacity of 100 MT will be set up by 2030. This will also help in reducing imports of natural gas, methanol, and ammonia. This move seeks to explore alternative energy pathways and reduce dependence on conventional sources.
- A phased mandatory blending of Compressed Natural Gas (CNG), Piped Natural Gas (PNG), and compressed biogas is on the agenda. This approach aims to create a more sustainable and environmentally friendly composition of gases used in various applications.
c. Empowering roofs through Solar: - Under the rooftop solarization initiative, the government aims to empower 1 Cr households by enabling them to generate up to 300 units of free electricity per month. This move encourages the widespread adoption of solar power at the household level.
- The initiative brings several advantages:
- Annual Savings: Significant savings of INR 15,000-18,000 per household annually through free solar electricity and surplus sales to distribution companies.
- Electric Vehicle Charging: Facilitates the convenient charging of electric vehicles, contributing to sustainable transportation solutions.
- Entrepreneurship Opportunities: Creates opportunities for numerous vendors, fostering entrepreneurship in the supply and installation sector.
- d. Upcoming Strategic Investment Opportunities for Green Energy
With such boost to the green energy sector, recently, REC, a Maharatna Central public sector enterprise under the Ministry of Power and Private Sector NBFC, National Investment and Infrastructure Fund Limited (NIIFL) signed an MOU to collaborate on a suite of funding solutions for renewable energy projects as well as large-scale projects across the country.
Source: The ET - India’s dynamic renewable energy sector is poised to attract over USD 250 Bn in investments.
Source: The EY Report October 2023 - As per reports, thematic investment opportunities in low-carbon initiatives, encompassing renewable power generation, energy storage, green hydrogen, ACC battery manufacturing, biofuels, and solar PV module manufacturing are expected to increase in the coming fiscals.
Source: The EY Report October 2023
Notably, the report highlights potential investments of approximately USD 15.5 Bn in solar PV manufacturing projects and around USD 2.7 Bn in India’s pursuits of advanced chemistry cell battery manufacturing. These insights underscore the nation’s strategic focus on diverse and sustainable energy solutions.
Source: The EY Report October 2023
E. Electric Vehicle Ecosystem
- The fast-growing EV market in India is catching the eye of global players. India’s electric vehicle market is expected to grow to 1 Cr units in annual sales by 2030 and create 5 Cr direct and indirect jobs, according to the Economic Survey 2022-23.
- As per industry estimates, the total EV sales in India stood at around 10 Lakh units in 2022. On the back of increasing EV demand, the Indian government is providing fiscal incentives to promote domestic manufacturing of these cars.
Source: The Mint - This shift underscores a strategic reallocation of resources towards incentivizing domestic manufacturing in the electric vehicle space.
The Government will expand and strengthen the e-vehicle ecosystem by:
- Supporting manufacturing and charging infrastructure.
- Greater adoption of e-buses for public transport networks will be encouraged through payment security mechanism.
- The government has reduced the FAME subsidy budget by 44% to INR 2,671 Cr for FY25, impacting the cost of EVs and potentially influencing demand.
- In contrast, the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for automobiles and auto components has surged by 623% to INR 3,500 Cr. While reduced subsidy may lead to a potential price increase, increased PLI schemes could result in cost savings for EV manufacturers which can be passed onto the customers thereby, stabilizing EV price points and demand.
4. Healthcare
The Economic Survey 2023 highlights the necessity of a significant boost in healthcare spending, forecasting an increase from 2.1% to beyond 2.5% of GDP by 2025.
There will be an increase in the number of hospitals and clinics dedicated to treating chronic diseases. The healthcare sector shall experience a significant growth with the promotion of innovative approaches and the integration of technology. This presents a substantial opportunity for research and development companies to create new medical devices, explore novel treatment methodologies, discover cures, and advocate for lifestyle changes.
In the era of Amrit Kaal for Bharat, the government aims to establish a Golden Disease-free era by leveraging technology, skilled medical professionals, and state-of-the-art infrastructure. Recognizing the importance physical as well as spiritual and mental health shall together foster a healthy and balanced lifestyle.
A. Establishment of Medical Colleges:
- The government of India has proposed to set up a special committee for the establishment of Medical Colleges in India by utilizing existing Hospital Infrastructure. The goal is to witness an increased number of medical students in the upcoming years.
- There has been an increase of 82% in medical colleges from 387 before 2014 to more than 704 colleges in 2023. Continuing similar growth trajectory, establishing new medical colleges and developed infrastructure facilities will contribute to the promotion of quality education and the presence of skilled medical practitioners in future.
Source: Government Press Release
B. Cervical Cancer Vaccination
- In an effort to reduce Cervical Cancer Cases in India, the government has committed to offer Vaccinations for Cervical Cancer. The government will encourage vaccinating girls in age group of 9 to 14 years.
- Cervical Cancer contributes to approximately 6-29% of all cancer cases in women.
Source: Hindustan Times - According to The Global Cancer Observatory (GLOBOCAN) 2020 estimates, India accounted for the highest number of cervical cancer cases in Asia.
Source: Mint - This initiative presents numerous opportunities for individuals and companies operating in the healthcare sector. Research and development firms can expand their budgets and redirect their focus toward finding a cure for cervical cancer. As a result, there may be a rising demand for specialized devices designed for the diagnosis and treatment of cervical cancer. Likewise, there is expected to be an increased demand for doctors specializing in this field.
- This initiative shall be a stepping stone to reducing cancer cases among women and making Bharat Cervical Cancer-free.
c. Maternal and Childcare
- The government has emphasized on improving maternal and Child healthcare by rolling out several schemes for their betterment. A comprehensive program will be launched to tackle issues related to maternal and childcare.
- Further, the government shall also upgrade Anganwadi centres under “Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0” Scheme which shall expedite improved nutrition delivery, early childhood care and development.
D. Safeguarding Health through Immunisation
- To facilitate immunisation against life-threatening diseases, the government shall promote vaccination of children through the newly designed U-WIN platform.
- The government had launched “Mission Indradhanush” back in 2014 with the objective to immunize children in India. By promoting this mission through the platform, the government will persistently work towards ensuring that the children of Bharat are immune and protected.
E. Ayushman Bharat
Following the footsteps of the Ayushman Bharat Mission, the government shall extend healthcare covers to ASHA workers, Anganwadi Workers and Helpers. The mission has empowered millions of families who could not afford premium healthcare services.
5. Tourism
- States are being encouraged to develop and endorse international- level tourist centres. Long-term interest-free loans will be extended to facilitate the financing of such developmental initiatives.
- India shall now be a recognised destination for business and conference tourism owing to the organisation of G20 in 60 regions of the country, that successfully presented India’s regional diversity to a global audience.
- Spiritual tourism is poised to gain impetus in India, with Ayodhya being the most recent example. This provides entrepreneurial opportunities for local businesses in numerous Tier II and Tier III cities across the country. In addition, the government is promoting hidden gems – the islands of India, strategizing tourism frameworks around these locales too.
- In effort to promote domestic tourism, the government has committed initiation of projects for port connectivity, tourism infrastructure and amenities development.
- Travel and tourism deal activity in India experienced a decline of over 16 % during the first half of 2023 and an overall drop of 7% YoY in deal activity across the industry.
Source: Economic Times - The travel market in India is projected to reach USD 125 Bn by fiscal year 2027 from an estimated USD 75 Bn in fiscal year 2020. Owing to the tailwinds of the budget this growth is poised to experience a positive surge. Moreover, startups focusing on developing solutions for the tourism sector including hotels, travel, hospitality, and its related facets are poised to witness a favourable market momentum in the upcoming year.
Source: India Brand Equity Foundation
6. Education
- The Skill India Mission has trained 4 Cr youth, upskilled and reskilled 54 Lakh youth, and established 3000 new Industrial Training Institute (ITIs). New institution set up for higher learning has been at a record high, with 7 IITs, 16 IIITs, 7 IIMs, 15 AIIMS and 390 universities being established by the current government. The set up of new universities and acclaimed higher learning institutions has created demand for the development of educational infrastructure, educational resources, and other disruptive educational solutions.
- The underlying proposition of the budget is focused on the fact that our prosperity depends on equipping and empowering the youth. Besides educational excellence, the country is witnessing growth in terms of sporting talent, with the highest ever medal tally in Asian Games and Asian Para Games in 2023.
- The budget highlighted the forthcoming period as the ‘golden era’ for the tech savvy youth as a corpus of INR 1 Lakh Cr will be established to provide long-term financing or refinancing requirements with long tenors and low or nil interest rates. This is set to significantly encourage research and innovation in India, as the Prime Minister endorses the “Jai Jawan, Jai Kisan, Jai Vigyan, Jai Anusudhan” as new India’s motto.
- In 2023, the number of funding rounds in edtech companies fell to 69 from 364 in 2021, and 242 in 2022. This downward trend may potentially reverse owing to the increased adoption of the National Education Policy 2020 and its focus on digital education. Moreover, as per the budget, female enrolment in higher education has gone up by 28% in 10 years, thus broadening the user base in the educational sector.
Source: The Hindu Business Line
- Post the budget, the educational sector can anticipate trends such as heightened digitization in education, a surge in demand for physical and digital educational infrastructure, innovative solutions to enhanced educational access in rural areas, and an increased emphasis on educational resources for higher education.
Conclusion
The 2024 Interim Budget, with a central emphasis on inclusive development, has touched upon pivotal sectors for concentrated growth and development as part of the transition towards the Viksit Bharat 2047 objective. Notably, the capital expenditure allocation has been increased by an auspicious 11.1% to Rs 11.11 lakh crore for the upcoming fiscal year. The budget underscored a focus on four major categories – Gareeb (poor), Mahila (women), Yuva (youth), and Annadatta (farmers), recognizing them as primary catalysts for building the foundation of Amrit Kaal.










 C. Existing Measures
C. Existing Measures


0 Comments